Galaxies / Stages of a Star's Life Cycle
- Due May 11, 2020 at 11:59pm
- Points 5
- Questions 5
- Time Limit None
- Allowed Attempts Unlimited
Instructions
Galaxies
- A galaxy is a huge system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust held together by gravity
- Galaxies are classified by their shape
- There are three types of galaxies - Spiral. Elliptical, and Irregular
Spiral Galaxies
- A flat, disk-shaped galaxy with a central bulge and "arms" that extend outward
-
We live in a spiral galaxy – The Milky Way

"Milkyway"
Elliptical Galaxies
- The most abundant type of galaxy that has a smooth, circular for an oval) shape Irregular Galaxies

Irregular Galaxies
- A random, scattered type of galaxy that does not form a distinct shape or pattern

Stars and Nebulas
Nebula- a huge cloud of dust and gas in space held together by gravity
Protostar - when nuclear fusion begins and a star gives off light for the first time
Main Sequence -90% of stars (including the Sun) are in this stage of their life cycle
Red Giant - the stage after the main sequence for a small to medium mass star; fuel begins to run out
Red Supergiant- the stage after the main sequence for a high mass star
White Dwarf - formed when a low-mass star has exhausted all its nuclear fuel and lost its outer layers Black Dwarf - a star that no longer gives off light or heat
Supernova - an explosion of a high mass star
Neutron Star-on extremely dense star that results from the gravitational collapse of a massive star after a supernova
Black Hole - a region of space having a gravitational field so intense that no matter or radiation can escape
Planetary Nebula - a ring-shaped nebula formed by an expanding shell of gas around an aging star
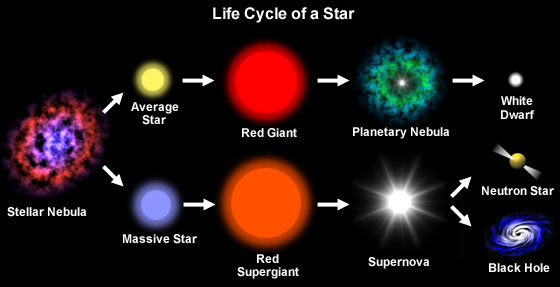
Stages of a Star's Life Cycle
- All stars go through the same first three stages - Nebula, Protostar, and Main Sequence
- After Main Sequence stage: Small to average mass stars like the Sun - Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, White Dwarf, Black Dwarf
- After the Main Sequence stage: High Mass Stars - Red Supergiant, Supernova, Neutron Star
- After Main Sequence stage: Extremely Massive Stars - Red Supergiant, Supernova, Black Hole
The mass of a star is the main factor that determines the path a star will take during its life cycle!