Ocean Systems
- Due May 25, 2020 at 11:59pm
- Points 4
- Questions 4
- Time Limit None
- Allowed Attempts Unlimited
Instructions
Human Dependence on Ocean Systems Humans depend on ocean systems for the following:
- Food - oceans provide fish and shellfish to large populations
- Water - oceans indirectly provide terrestrial (land) life with fresh water through the water cycle
- Transportation-oceans provide an efficient way to transport goods on ships
- Climate Regulation - ocean currents circulate warmer water from the equator to arctic regions and cooler water from arctic regions to the equator; currents help to moderate temperature extremes
- Recreation - boating, fishing, diving, and surfing
Negative Human Impact on Ocean Systems Humans negatively impact ocean systems in the following ways:
- Overfishing-populations of fish and shellfish are dropping quickly because they are being removed from oceans faster than they are able to reproduce
- Runoff and Pollution-toxic chemicals from factories runoff into rivers and end up in the ocean; these toxic chemicals can kill fish or make them potentially dangerous for human consumption; fertilizers and pesticides wash off into rivers and are carried into the ocean
- Habitat Destruction-many wetlands and other habitats have been destroyed by human developments and pollution
Positive Human Impact on Ocean Systems Humans positively impact ocean systems in the following way:
1. Artificial Reefs - humans create artificial reefs by sinking old ships, train cars, and other non-toxic structures; these artificial reefs help to support large fish populations and new food webs; artificial reefs support lite much like naturally occurring coral reefs

Watershed
- An area of land where all of the water that is under it or drains off of it goes into the same place
- Human activities can have a significant impact on Earth's water systems
- Surface Water - water on the surface of Earth such as a river, stream, lake or ocean
- Ground Water - water present beneath the Earth's surface
- Runoff has increased due to more roads, houses, and buildings being constructed
- Improper disposal of trash can eventually make its way into the ocean or other water systems
- Fertilizers eventually make their way into ground or surface water
- Excess fertilizers or other forms of pollution can spread to other areas as they travel along the watershed
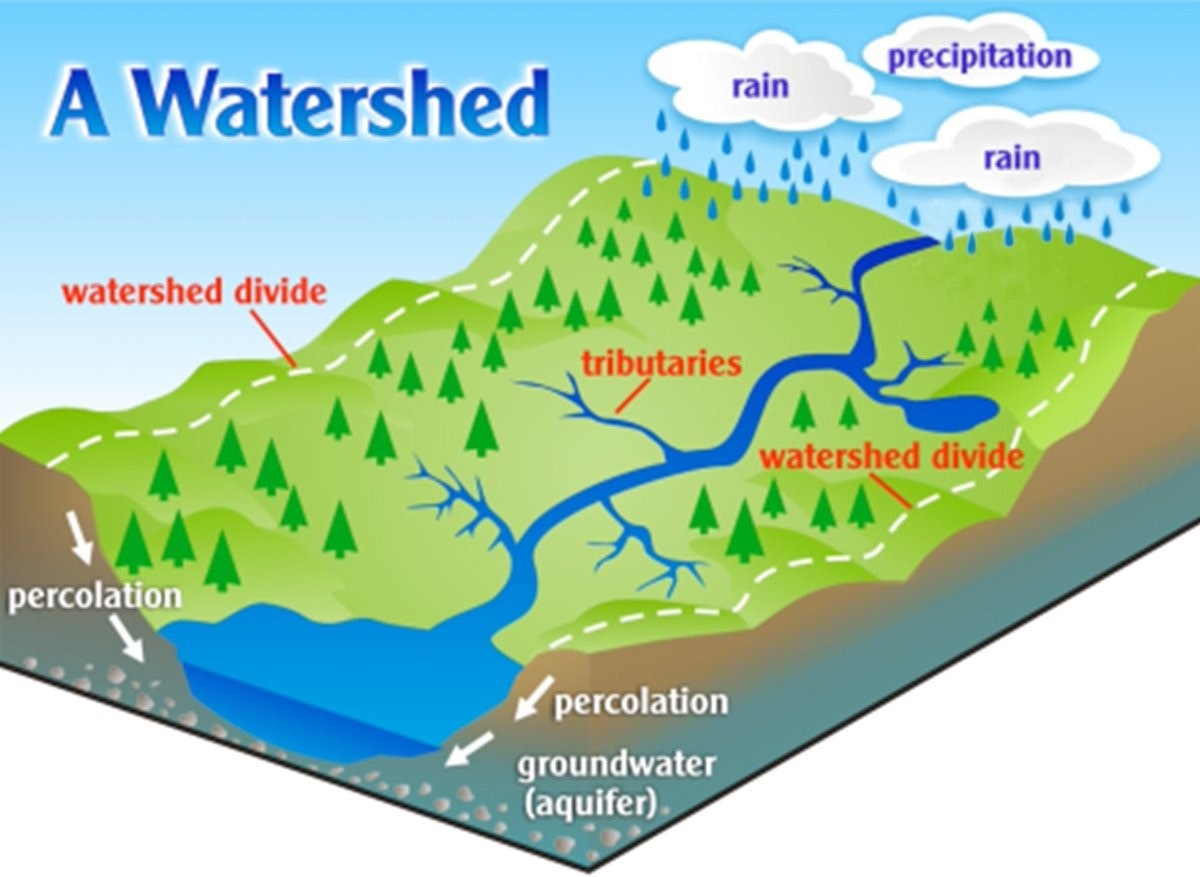
Ground Water
- Found within on aquifer
- Aquifer-a layer of rock or soil that can hold water

- An aquifer consists of permeable material - water is able to move through the material
- Impermeable -a layer of material that does not allow water to move through (ex. Bedrock)

- Water held within an aquifer is known as a saturated zone
- The top of a saturated zone is known as a water table - the water table will change as the level of water in an aquifer changes
Primary vs Secondary Succession
-
Primary succession occurs following an opening of pristine habitat, examples:
- Oil spills
- Glaciers melting and retreating
- Volcanic eruptions

primary succession usually takes a long time, hundreds of years
-
Secondary succession is a response to a disturbance, whereby newer communities are created after the event. examples:
- After forest fires
- tsunamis

secondary succession usually takes a short time, following some natural disaster